Synple Automatic Synthesizer & Reagent Cartridges
Introduction
Routine organic synthesis often requires extensive reagent preparation, manual handling, and repeated purification steps that introduce variability and consume significant laboratory time. Synple 2 Automated Synthesizer addresses these challenges by standardizing routine organic synthesis through single-use reagent cartridges and optimized, system-controlled workflows. The instrument integrates automated reaction handling, work-up, and purification within a compact benchtop unit, providing a reproducible and low-contact alternative to traditional manual synthesis. The platform enables consistent performance across a broad set of reaction classes by combining pre-measured reagents, programmable fluidics, and controlled reaction environments.
Synple 2 Workflow
- Select the starting material.
- Insert the pre-filled Synple reaction cartridge.
- Confirm the method and press Start.
- Allow the system to run the reaction, work-up, and isolation automatically.
- Collect the purified product from the collection vial.
- Let the wash sequence complete to prepare the instrument for the next synthesis.
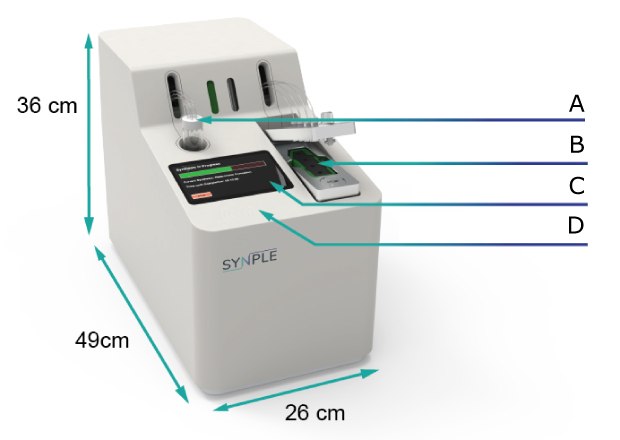

Synple 2 Automated Synthesizer. A) Sample holder; B) Cartridge holder;
C) Touchscreen; D) Cartridge scanner
- The instrument has a compact benchtop footprint of 49 cm by 26 cm with a height of 36 cm.
- The sample holder is positioned on the upper surface and secures the vial containing the dissolved starting material.
- The cartridge holder locks the pre-filled reagent cartridge into position for operation.
- The touchscreen interface provides method selection, parameter confirmation, and run monitoring.
- The cartridge scanner reads the RFID chip embedded in each cartridge and loads the corresponding pre-programmed protocol.
Synple 2 Synthesizer Setup
The internal architecture of Synple 2 Automated Synthesizer integrates precision fluidics and automated control to deliver reproducible reaction outcomes.
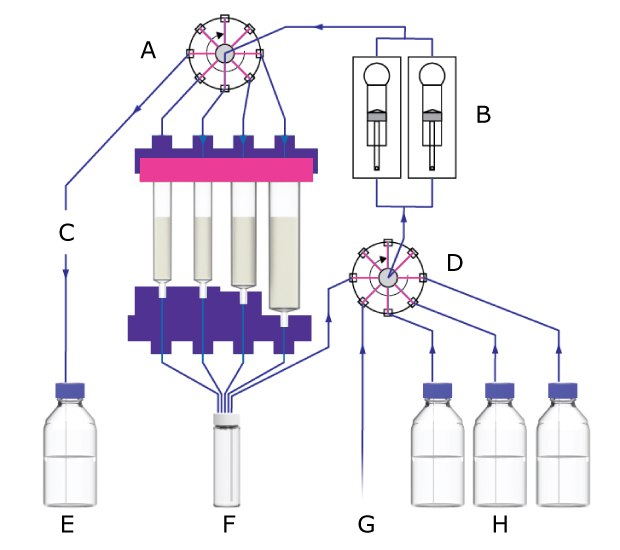
Figure 3.Synple 2 synthesizer set-up. A) Valve 1; B) Pumps; C) Capsule with four compartment; D) Valve 2; E) Waste; F) Sample vial; G) N2 supply;
H) Solvents
The Synple 2 synthesizer setup includes the core components responsible for moving reagents, directing flow paths, and controlling each stage of the automated workflow. These elements together form the operational framework described in the following list.
- Two syringe pumps for accurate solvent and reagent delivery
- Two rotary valves that manage solvent routing and control the flow path
- Defined fluidic connections between the sample vial, cartridge compartments, solvent lines, and waste container
- Automated steps for reagent addition, mixing, reaction progression, washing, and purification
- Embedded control logic linked to the RFID scanner for standardized method execution
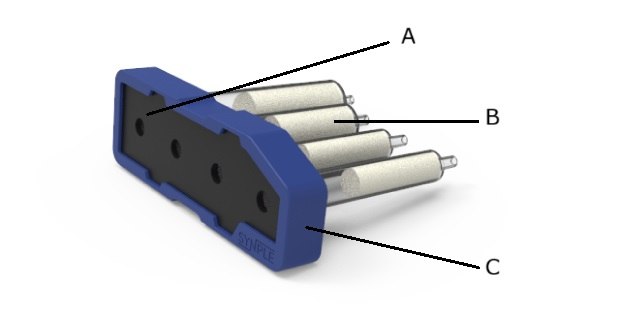
Synple 2 reaction cartridge.
A) Chemical resistant seal
B) Components preloaded with reagents
C) RFID chip programmed with reaction sequence
Synple reaction cartridges are designed as ready-to-use modules that contain all necessary reagents and built-in guidance for each synthesis. These cartridges are offered for a variety of reactions. Each cartridge contains all the reagents required to generate, isolate, and purify the reaction products, as well as an RFID chip encoded with the reaction method.
- Chemical-resistant seal: Protects reagents and prevents solvent leakage.
- Pre-loaded reagent compartments: Contains all reagents needed for the reaction, work-up, and purification.
- RFID chip: Automatically loads the correct reaction method into the instrument.
N-Heterocycle Synthesis

N-heterocycle formation cartridge
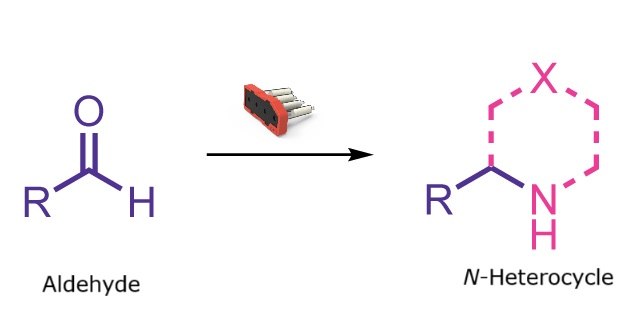
N-heterocycle formation reaction
This reaction class enables the automated synthesis of N-heterocycles such as morpholines, piperazines, oxazepanes, diazepanes, and a variety of more complex spiro and bicyclic structures. A wide range of structurally and electronically diverse aldehydes can be efficiently converted into the corresponding N-heterocycles with a simple setup that requires only about 10 minutes of user time.
Key details
- Ten N-heterocycle structures currently supported
- Scale up to 0.5 mmol
- The cartridge contains all reagents and catalysts required for imine formation, cyclisation, and purification
Benefits over classical batch synthesis
- Reduced user exposure to toxic tin reagents
- Multistep transformations completed automatically at the press of a button
- High reproducibility across runs
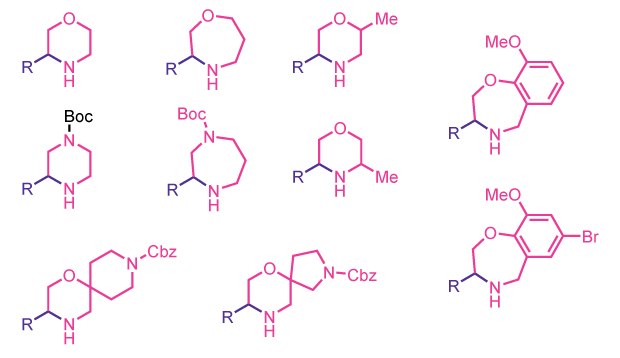
10 different N-Heterocycles forming cartridges available
N-Heterocycle Formation Cartridges
Reductive Amination

Reductive amination cartridge
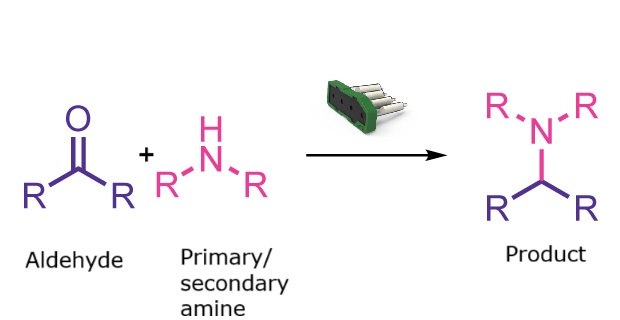
Reductive amination reaction
This reaction class supports automated reductive amination for the efficient synthesis of complex amines. Aldehydes or ketones can be combined with primary or secondary amines to generate a broad range of amine products with minimal user input.
Key Details
- Reaction scale up to 0.5 mmol
- The cartridge contains all reagents required for the condensation, reduction, and purification steps
- Compatible with diverse carbonyl and amine partners
Benefits Compared to Classical Batch Chemistry
- Time saving: reaction, work-up, and purification completed in a single automated process
- Automates routine chemistry, allowing users to focus on more demanding work
- Generic methods selected based on reaction partners, reducing the need for reaction optimization
Reductive Amination Cartridge
PROTAC Formation

PROTAC cartridge
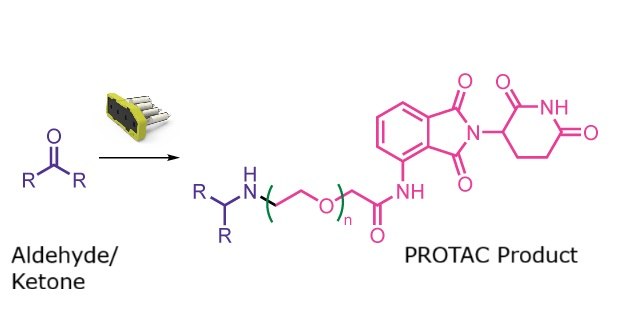
PROTAC formation reaction
This reaction class supports automated formation of PROTAC molecules. Both VHL and CRBN ligands are available with PEG linkers of different lengths, enabling flexible design of linker–ligand architectures for targeted protein degradation applications.
Key Details
- Reaction scale up to 0.1 mmol
- Cartridge contains all reagents required to link the carbonyl group of a protein binder to the partial PROTAC
- Includes purification components to streamline product isolation
- Supports coupling of amines, carboxylic acids, ketones, and aldehydes
- Cartridges available for reductive amination and amide bond formation
PROTAC Formation Cartridges
Biotin Tag Formation

Biotin cartridge
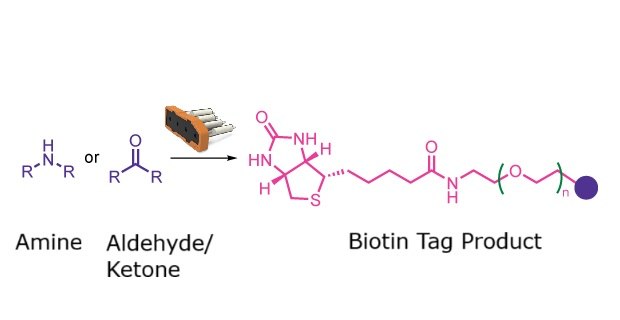
Biotin tag synthesis reaction
This reaction class supports the attachment of biotin tags to amines and aldehydes or ketones. A selection of PEG linker lengths is available, enabling flexible design of biotinylated molecules for probe development or affinity applications.
Key Details
- Reaction scale up to 0.1 mmol
- The cartridge contains all reagents required to link the compound of choice to a variety of biotin tags
- Includes purification components to enable simple and efficient product isolation
- Compatible with both amine substrates and carbonyl-containing substrates
Biotin Tag Cartridges
Mitsunobu Reaction

Mitsunobu cartridge
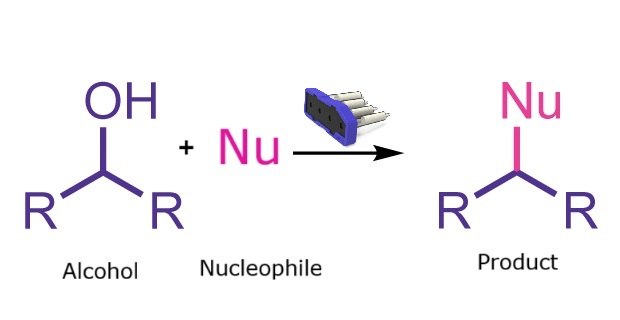
Mitsunobu reaction
The Mitsunobu reaction, first reported in 1967, is widely used in organic synthesis and medicinal chemistry due to its broad scope, stereoselectivity, and mild conditions. It enables efficient carbon–carbon bond formation through dehydrative coupling of a primary or secondary alcohol with a pronucleophile. Traditional batch methods, however, can generate byproducts that complicate purification. Running the reaction on the Synple platform minimizes these drawbacks and streamlines the overall process.
Key Details
- Reaction scale from 0.2 to 0.5 mmol
- Compatible with a wide range of pronucleophiles, including phenols, phthalimides, tosylamides, tosylhydrazones, and carboxylic acids
- The cartridge contains all reagents required to perform the complete Mitsunobu sequence
- Only 5 to 10 minutes of setup time required to obtain the Mitsunobu product
- No tedious removal of triphenylphosphine oxide (PPh₃O)
Mitsunobu Reaction Cartridge
Amide formation

Amide cartridge
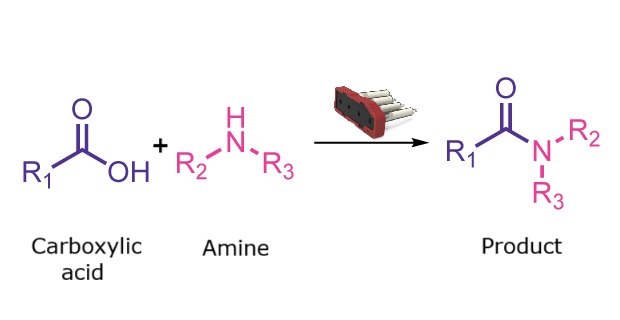
Amide formation reaction
Traditional amide formation involves activation of a carboxylic acid with a coupling agent to generate a reactive intermediate that is subsequently attacked by an amine. Although many coupling agents are commercially available, increased awareness of their potential as skin sensitizers has driven interest in safer alternatives. Solid-supported coupling agents offer an effective solution by reducing user exposure and simplifying purification. The Synple synthesizer enables automated amide formation using this approach.
Key Details
- Reaction scale up to 0.5 mmol
- The cartridge contains all reagents required for carboxylic acid activation, coupling, and purification
- Solid-supported coupling agents minimize exposure to sensitizing chemicals
- Automated workflow simplifies and standardizes amide bond formation
Amide Formation Cartridge
Deoxyfluorination

Fluorination cartridge
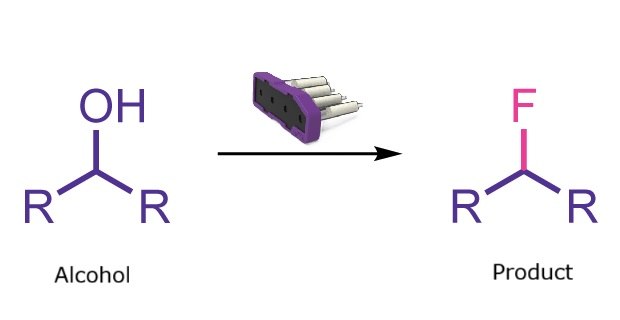
Deoxyfluorination reaction
Fluorination reactions play a key role in medicinal chemistry and are frequently applied in late-stage functionalization. Deoxyfluorination, a specific subset of these reactions, converts primary or secondary alcohols into the corresponding fluorinated products through reaction with a fluorinating agent. The Synple synthesizer enables this transformation through an easy and fast automated workflow that avoids direct handling of fluorinating agents.
Key Details
- Reaction scale-up to 0.2 mmol
- Suitable for primary and secondary alcohols
- The cartridge contains all reagents required for the complete deoxyfluorination sequence
- Eliminates user exposure to fluorinating agents while ensuring reproducibility
Deoxyfluorination Cartridge
Boc Protection

Boc protection cartridge
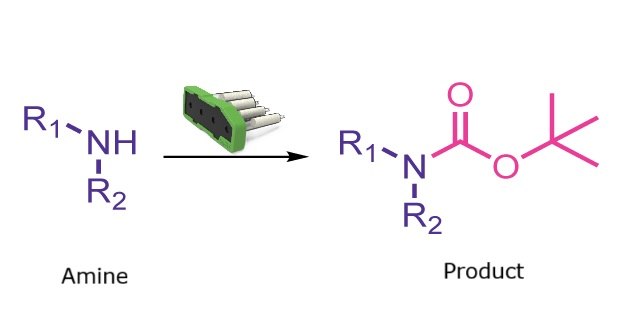
Boc protection reaction
N-Boc protection is one of the most widely used strategies for protecting amines in synthetic chemistry. The Synple synthesizer provides a simple and rapid automated method to Boc-protect primary and secondary amines. The process requires less than 5 minutes of user time and avoids any leftover Boc anhydride.
Key Details
- Two cartridge sizes available
- Up to 0.5 mmol
- Up to 1.2 mmol
Boc Protection Cartridges
Cbz Protection
Cbz protection cartridge
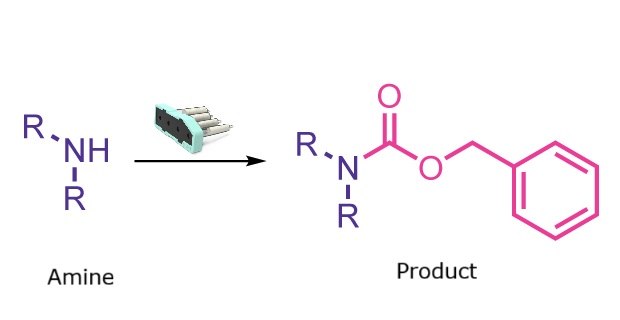
Cbz protection reaction
Cbz protection is valued for its stability toward acidic, basic, and oxidative conditions and its compatibility with many electrophilic reagents. However, traditional Cbz installation using benzyl chloroformate (Cbz-Cl) involves safety concerns due to its toxicity, lachrymatory nature, and strong odor. It also typically requires a basic aqueous workup to remove excess Cbz-Cl, making the process more laborious.
Using Cbz-OSu as a safer alternative eliminates these hazards. With the Synple synthesizer and the pre-packed Cbz-OSu cartridge, N-Cbz protection becomes a fast, automated, and user-friendly process.
Key Details
- Reaction scale up to 0.8 mmol
- Suitable for primary and secondary amines and amine salts
- The cartridge contains all reagents needed for Cbz installation and purification
- Uses Cbz-OSu as a safer, non-toxic alternative to Cbz-Cl
- Simplifies the workflow by avoiding corrosive, volatile reagents and eliminating aqueous workup steps
Cbz Protection Cartridge
Nosyl Potection

Nosyl protection cartridge
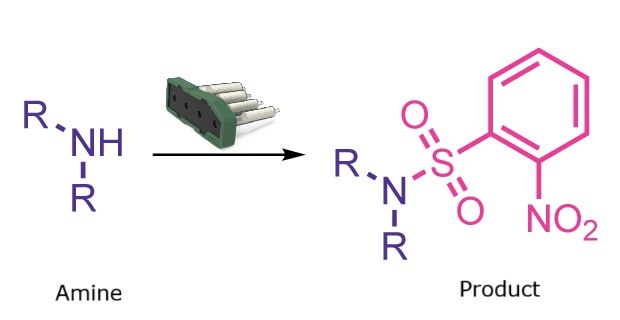
Nosyl protection reaction
Amino groups are common in small molecules, peptides, and proteins and often require protection during multistep synthesis to block unwanted reactivity and improve handling or purification. While carbamate-based protecting groups such as Boc, Cbz, and Fmoc are widely used, nitrobenzenesulfonamides (Nosyl or Ns groups) provide an effective alternative.
Ns protecting groups offer several advantages, including stability under acidic and basic conditions, straightforward installation and removal, and the ability to activate primary amines for the synthesis of secondary amines. Traditional Ns installation, however, uses o-Ns-Cl (2-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride), a corrosive reagent that poses significant safety risks and typically requires a basic aqueous workup to remove excess reagent.
With the Synple synthesizer and the pre-packed o-Ns-Cl cartridge, Ns protection becomes safer, cleaner, and more user-friendly through automated synthesis and solid-phase purification.
Key Details
- Reaction scale up to 0.8 mmol
- Suitable for primary and secondary amines and amine salts
- Cartridge contains all reagents required for Ns installation and purification
- Avoids direct handling of corrosive reagents such as o-Ns-Cl
- Eliminates labor-intensive aqueous workup steps through solid-supported purification
Nosyl Protection Cartridge
Boc Deprotection

Boc deprotection cartridge
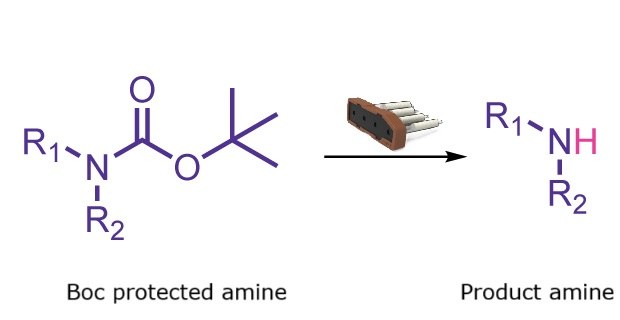
Boc deprotection reaction
N-Boc deprotection converts an N-Boc protected amine into the corresponding free amine salt through reaction with an acid such as TFA, HCl, or TsOH. The Synple synthesizer provides a fast and automated method for deprotecting primary and secondary amines while avoiding direct handling of volatile and corrosive acids.
Key Details
- Reaction scale up to 0.5 mmol
- Suitable for primary and secondary amines
- The cartridge contains all reagents required for the deprotection and purification steps
- Eliminates user exposure to corrosive and volatile acids such as TFA or HCl
Boc Deprotection Cartridge
Silyl Deprotection

Silyl deprotection cartridge
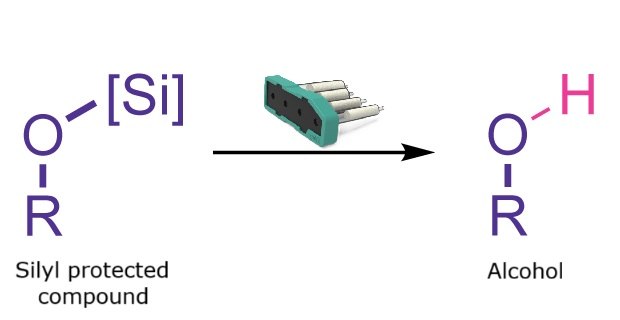
Silyl deprotection reaction
Silyl deprotection converts a silyl-protected alcohol into the corresponding free alcohol. This transformation is widely used in organic synthesis and is typically performed using acids such as TFA, HCl, or CSA, or fluoride sources such as TBAF or HF pyridine. The Synple synthesizer provides a fast and automated method for deprotecting primary and secondary alcohols while avoiding direct handling of volatile, corrosive acids or fluoride reagents.
Key Details
- Reaction scale up to 0.5 mmol
- The cartridge contains all reagents required for the deprotection and purification steps
- Eliminates user exposure to corrosive acids and fluoride reagents such as TFA, HCl, or TBAF
Silyl Deprotection Cartridge
Suzuki Coupling
Suzuki coupling cartridge
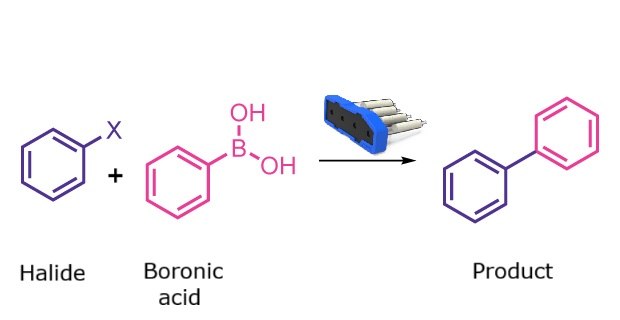
Suzuki coupling reaction
Palladium-catalyzed Suzuki–Miyaura coupling enables carbon–carbon bond formation through the coupling of an aryl halide with an aryl boronic acid. After manual loading of the starting materials into the reaction vessel, the Synple synthesizer performs the entire reaction sequence, including the coupling, work-up, and product isolation, without further user involvement. This provides a streamlined route to biaryl products.
Key Details
- Reaction scale up to 0.8 mmol
- Supports the coupling of aryl bromides, with aryl chlorides also possible
- Compatible with a wide range of aryl boronic acids
- The cartridge contains catalyst, reagents, and purification components
Suzuki Coupling Cartridge
Related Resources
- Brochure: Synthesis Made Synple - Synple Chem - Automated Chemical Synthesis Platform
Download the brochure to get a detailed overview of the Synple 2 system, including its specifications, workflow steps, compatible cartridges, supported reaction types, setup instructions, and performance data.
To continue reading please sign in or create an account.
Don't Have An Account?